Connecting Mastra agents to Gram-hosted MCP servers
Mastra is a TypeScript framework for building AI-powered applications. Its MCP client lets you connect agents to external tools and APIs. This guide shows you how to connect a Mastra agent to a Gram-hosted MCP server using an example Push Advisor API.
By the end, you’ll have a workflow that uses natural language to check whether it’s safe to push to production.
Find the complete code and OpenAPI document in the Push Advisor API repository .
Prerequisites
To follow this tutorial, you need:
- A Gram account
- An OpenAPI API key
- A Node.js environment set up on your machine
Creating a Gram MCP server
If you already have a Gram MCP server configured, you can skip to connecting Mastra to your Gram-hosted MCP server. For an in-depth guide to how Gram works and a demonstration of how to create a Gram-hosted MCP server, check out the Gram concepts guide.
Setting up a Gram project
In the Gram dashboard , click New Project to create a new project. Enter a project name and click Submit
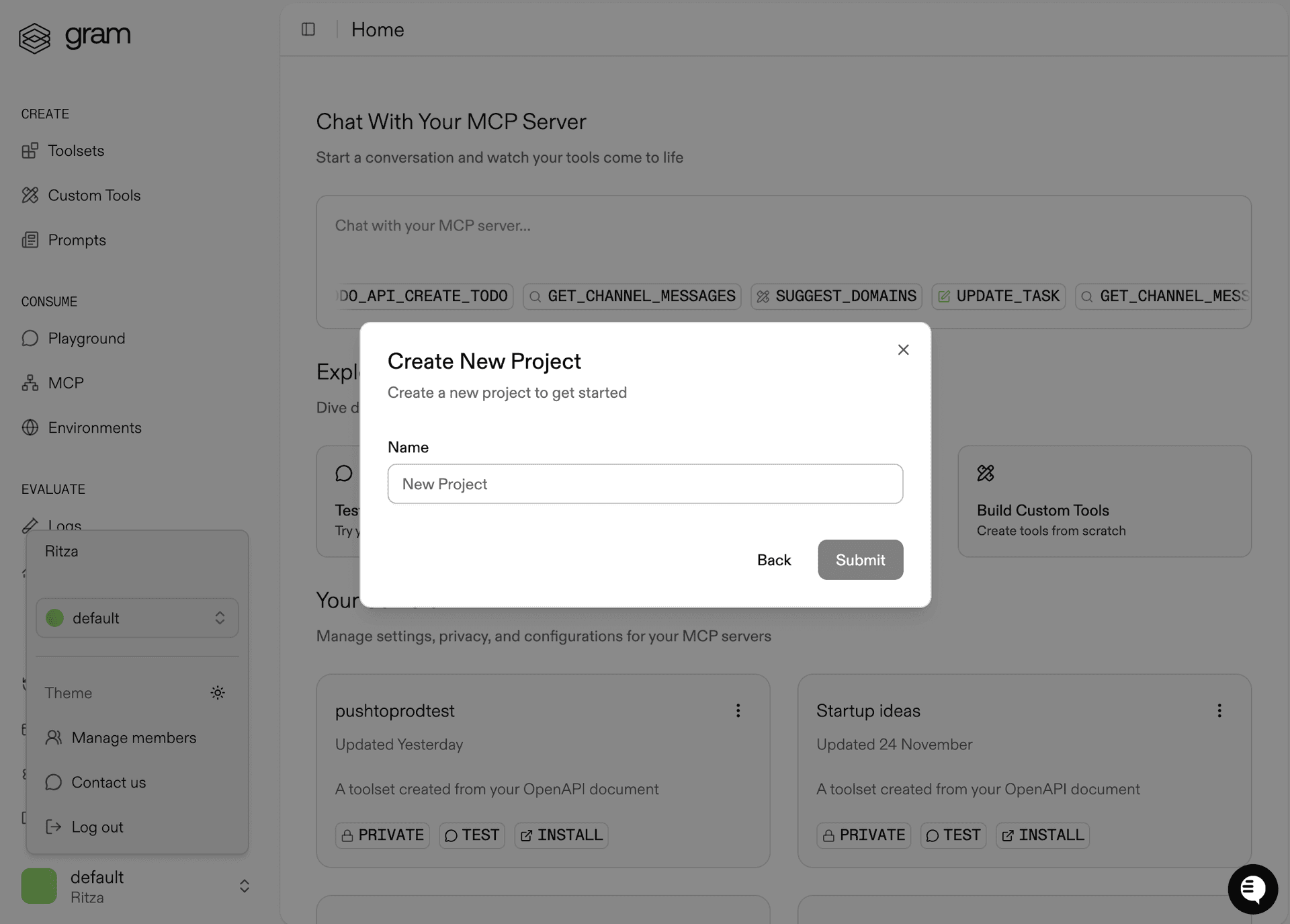
Once the project is created, click the Get Started button.
Choose Start from API. Gram will then guide you through the following steps.
Step 1: Upload the OpenAPI document
Upload the Push Advisor OpenAPI document , enter the name of your API, and click Continue.
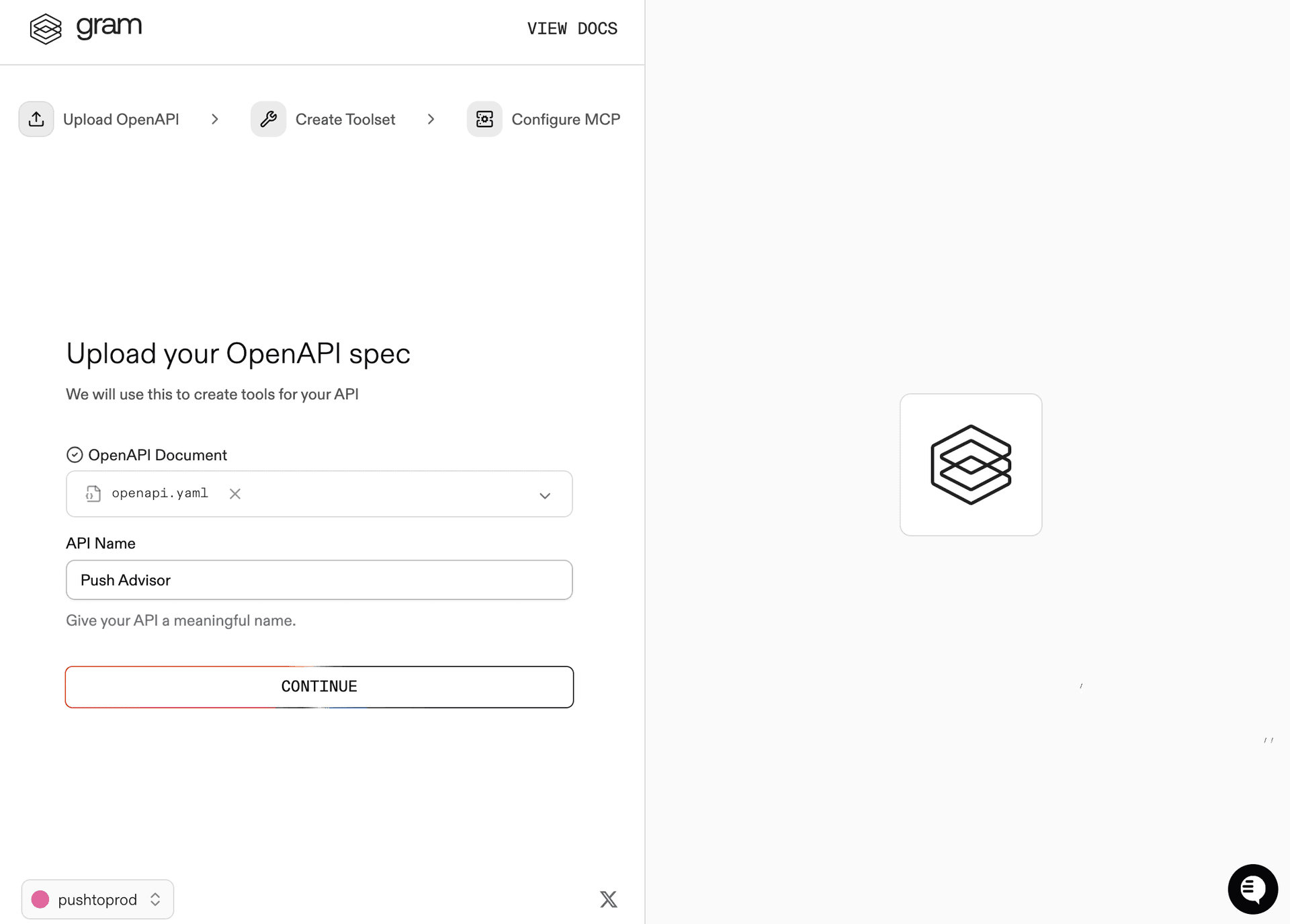
Step 2: Create a toolset
Give your toolset a name (for example, Push Advisor) and click Continue.
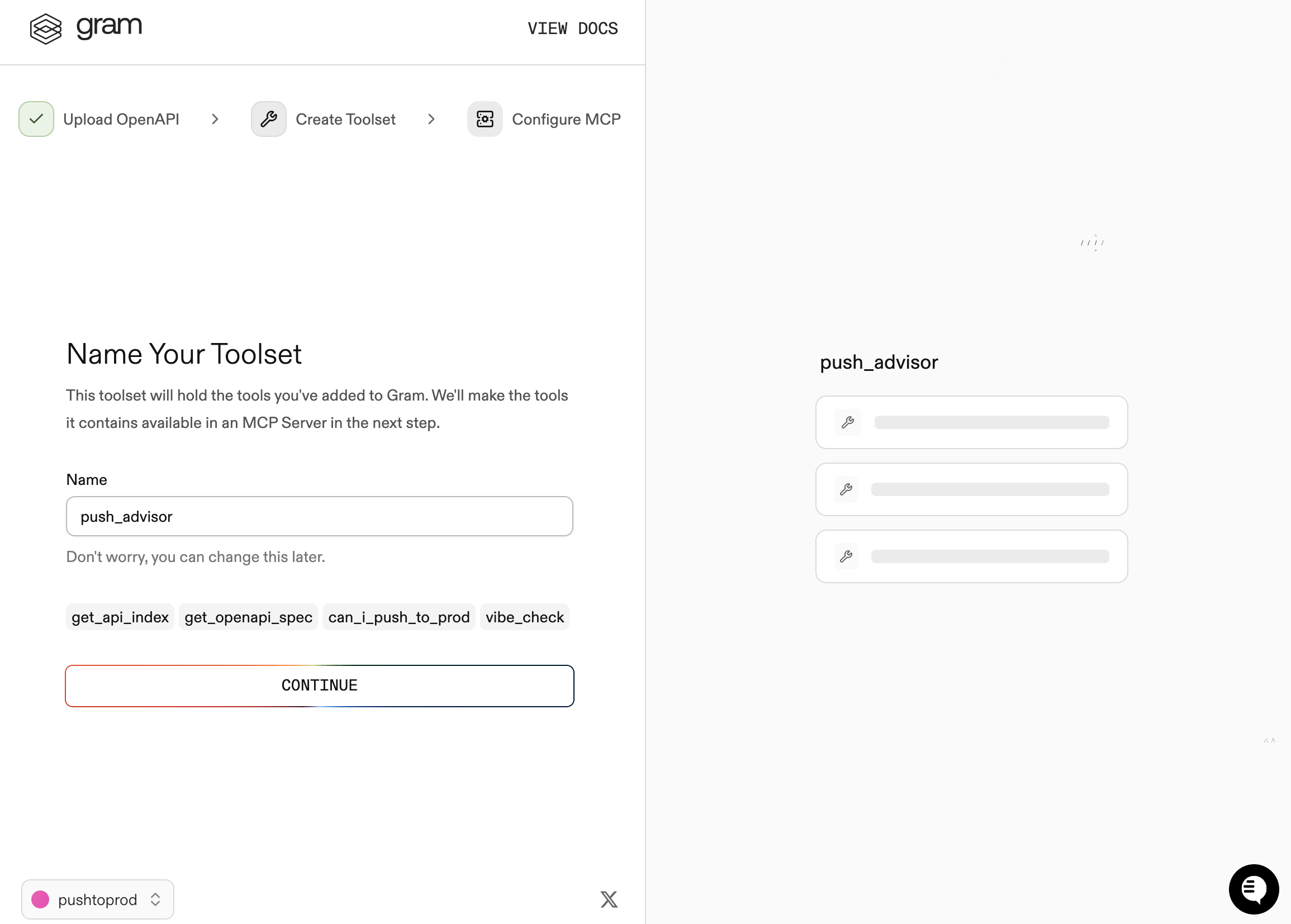
Notice that the Name Your Toolset dialog displays the names of the tools that Gram will generate from your OpenAPI document.
Step 3: Configure MCP
Enter a URL slug for the MCP server and click Continue.
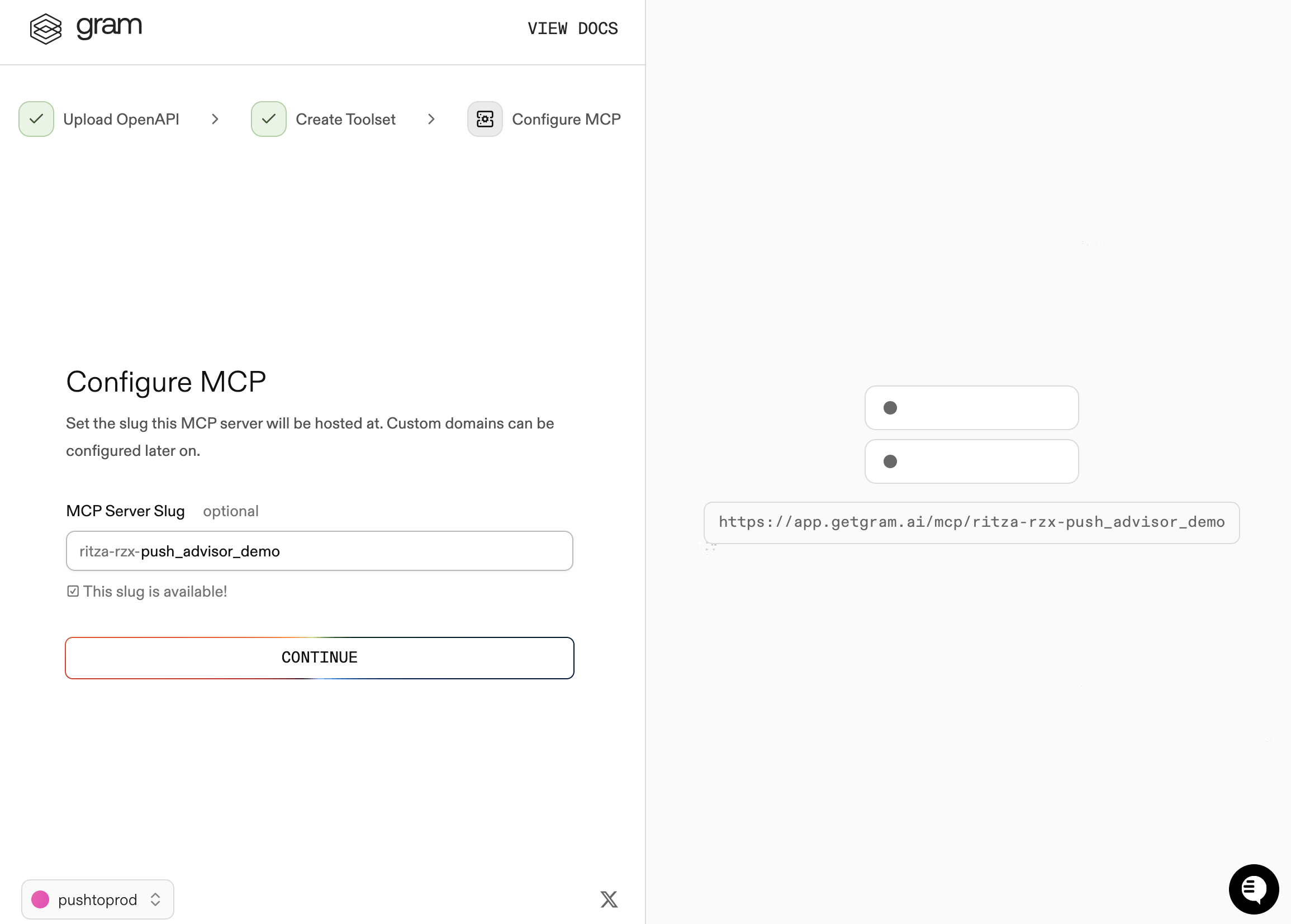
Gram creates a new toolset from the OpenAPI document.
Click Toolsets in the sidebar to view the Push Advisor toolset.
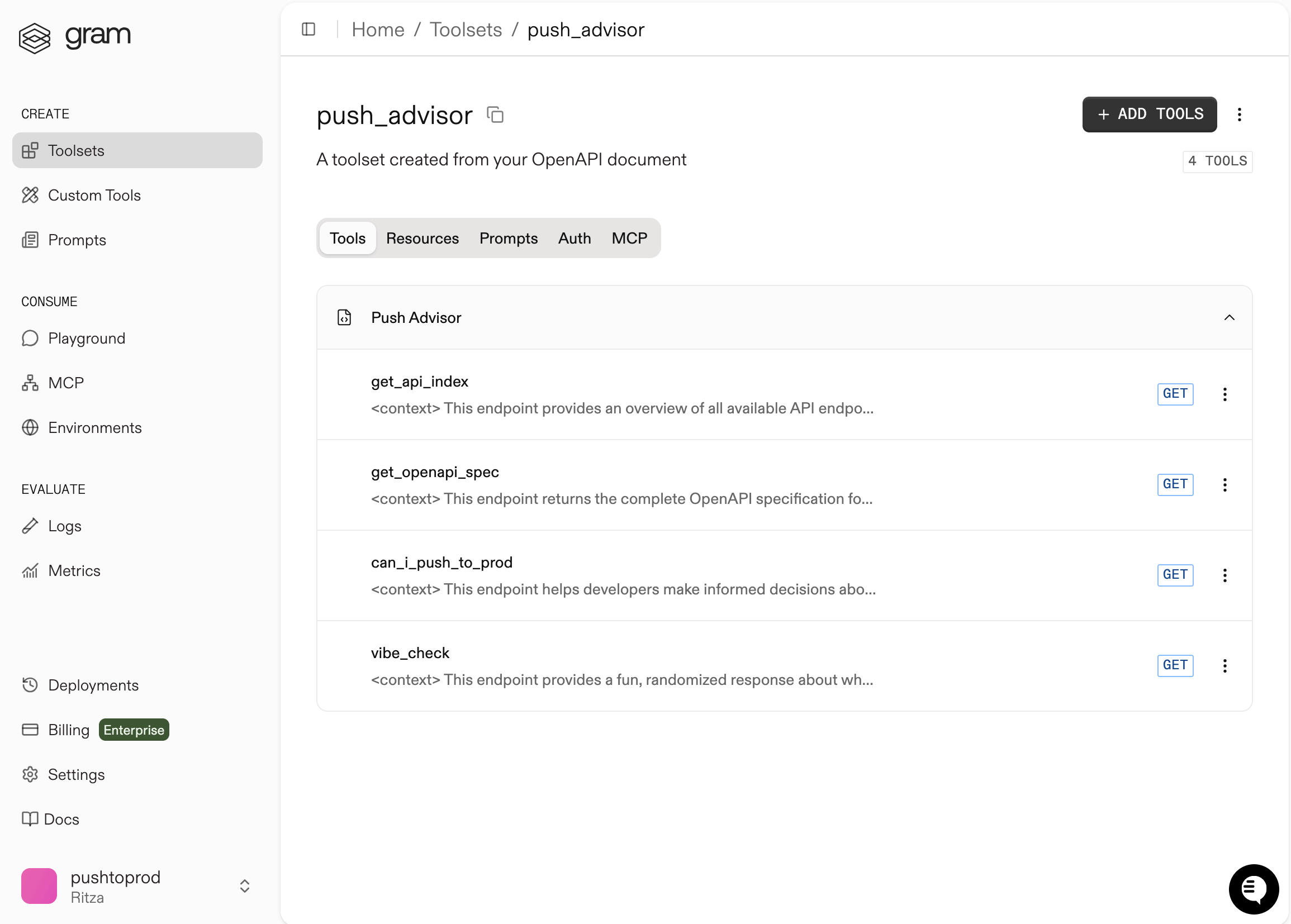
Configuring environment variables
Environments store API keys and configuration separately from your toolset logic.
In the Environments tab, click the Default environment. Click Fill for Toolset. Select the Push Advisor toolset and click Fill Variables to automatically populate the required variables.
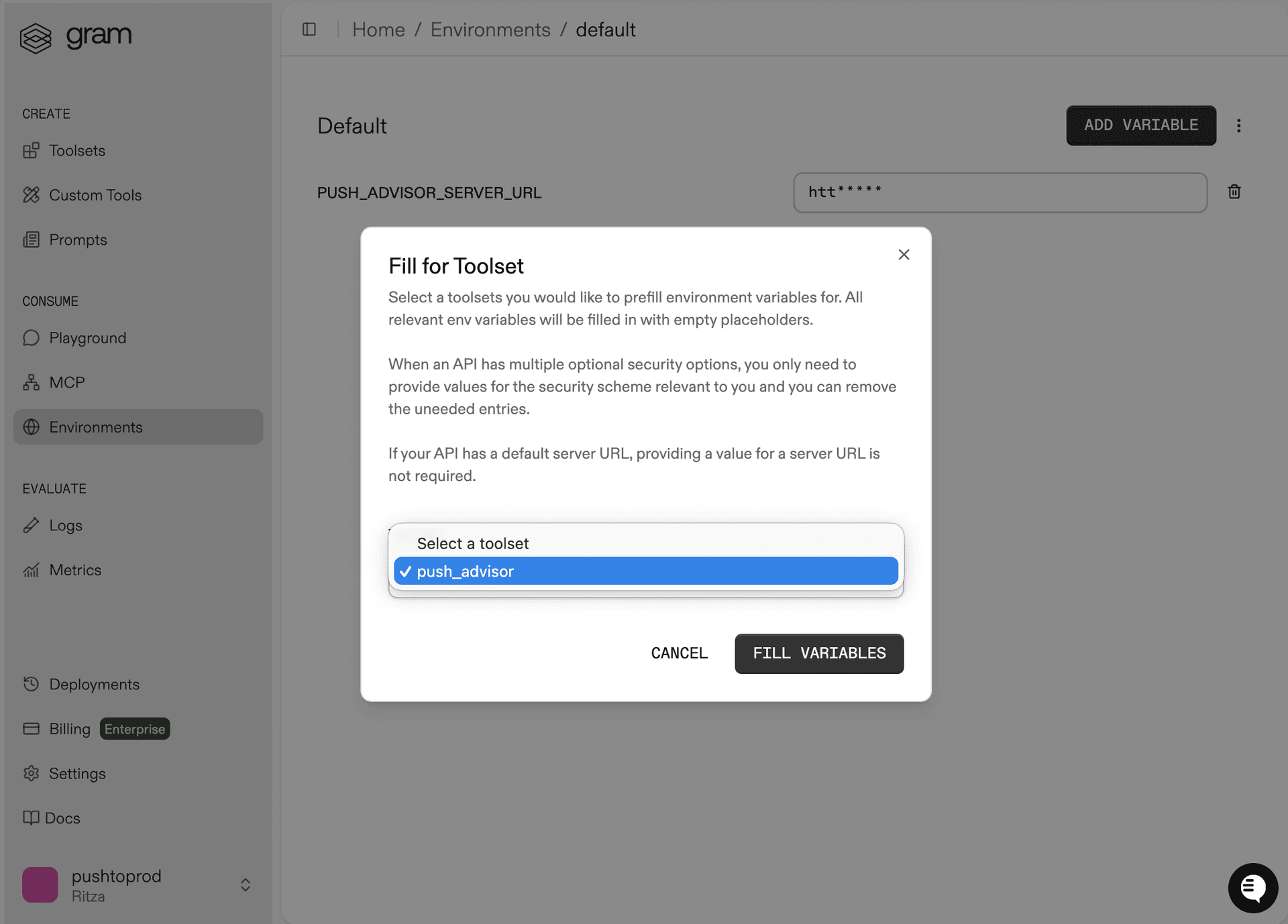
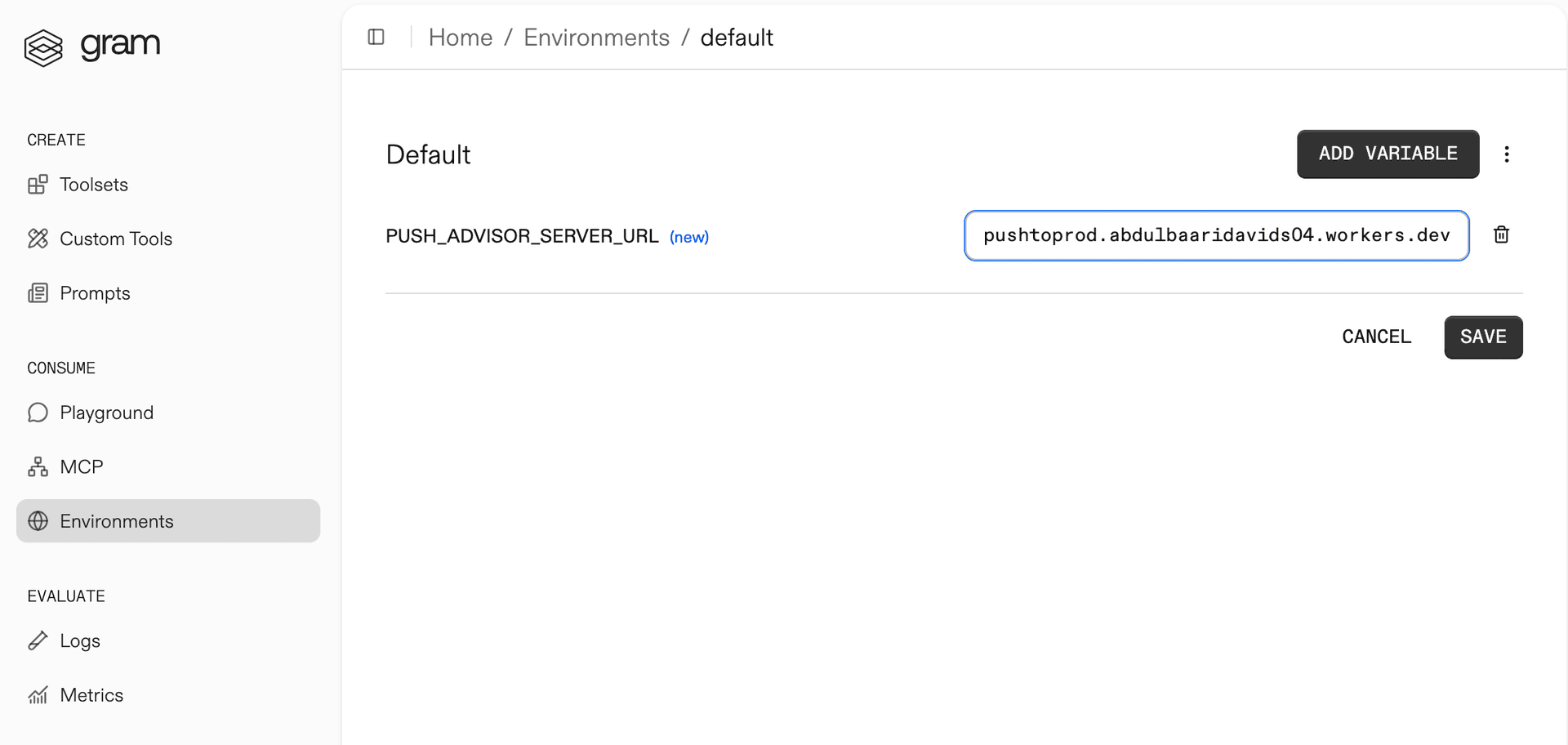
The Push Advisor API is hosted at https://canpushtoprod.abdulbaaridavids04.workers.dev, so set the <your_API_name>_SERVER_URL environment variable to https://canpushtoprod.abdulbaaridavids04.workers.dev. Click Save.
Publishing an MCP server
Let’s make the toolset available as an MCP server.
Go to the MCP tab, find the Push Advisor toolset, and click the title of the server.
On the MCP Details page, click Enable and then Enable Server to enable the server.
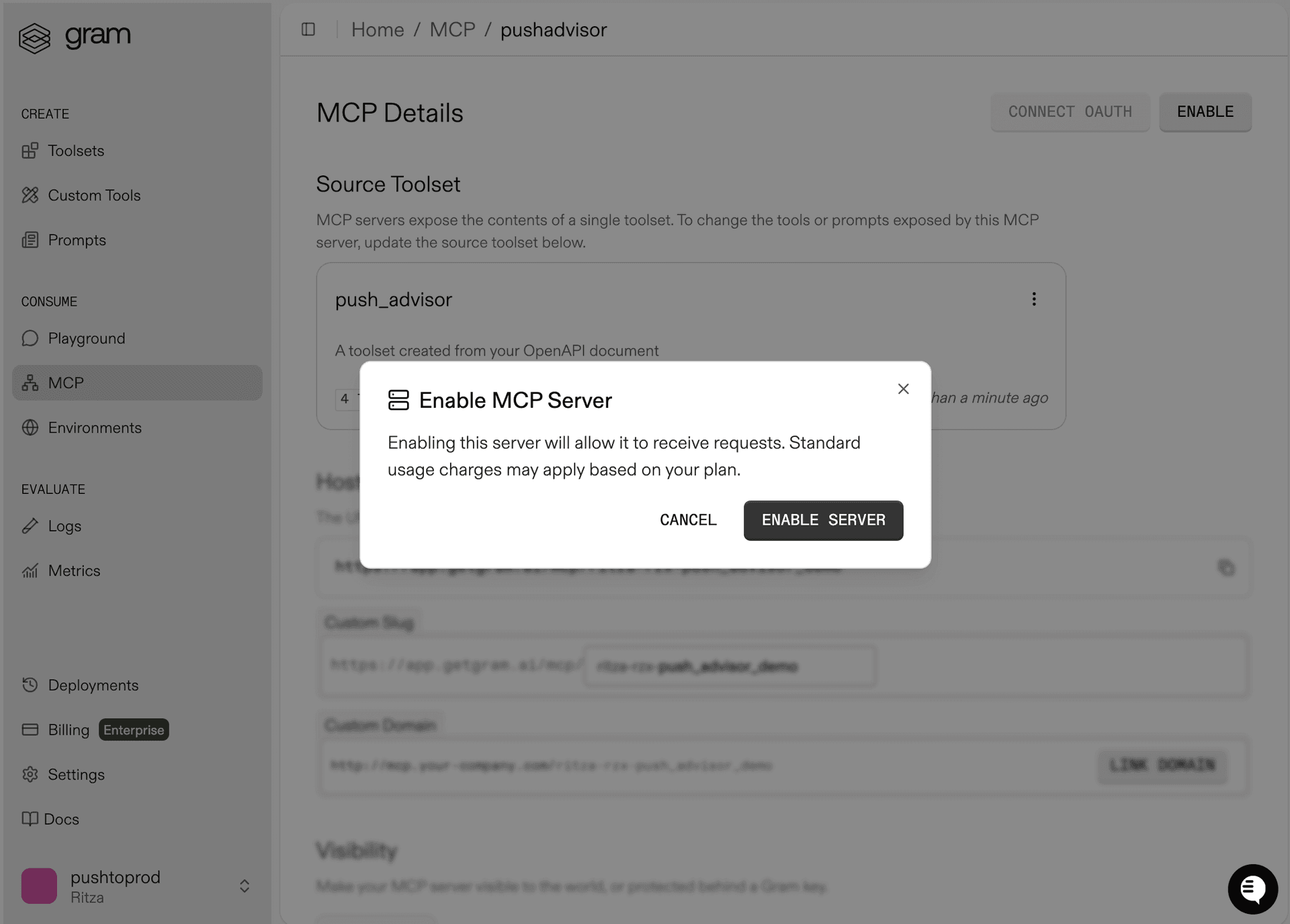
Take note of your MCP server URL in the Hosted URL section.
Generate a GRAM API key in the Settings tab.
Connecting Mastra to your Gram-hosted MCP server
This section covers creating a Mastra project and configuring it to connect to a Gram-hosted MCP server.
Project setup
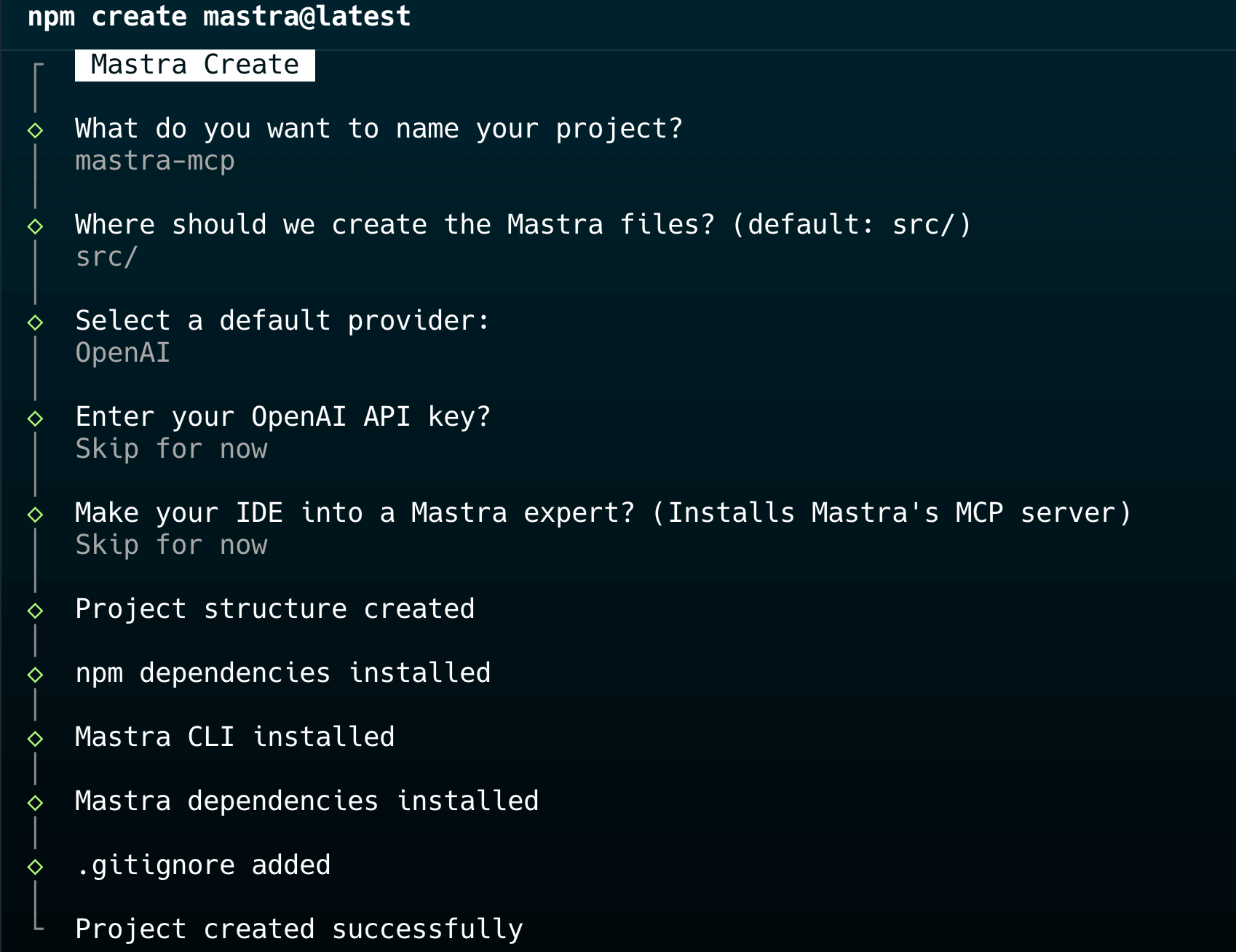
Run the following command to create a Mastra project:
npm create mastra@latestYou will be prompted to provide the following information:
- The project name: Enter
mastra-mcp. - The destination for the Mastra files: Press
Enter. - The default provider: Select
OpenAI. - The OpenAI key: Enter the OpenAI key.
Press Enter to accept the default options for the remaining prompts.
After the project is created, create a .env.local file and add your API keys:
GRAM_KEY=your-gram-api-key-here
OPENAI_API_KEY=your-openai-api-key-hereInstall the MCP dependencies:
npm install '@mastra/mcp@^0.14.4' '@ai-sdk/openai@^1.0.0' 'dotenv@^16.4.5' --legacy-peer-depsThis installs the MCP client library, OpenAI SDK adapter, and dotenv for environment variables. The --legacy-peer-deps flag resolves a version conflict: the Mastra CLI installs zod@^4.1.13, but @ai-sdk/openai@^1.0.0 requires zod@^3.0.0. Both versions are compatible at runtime.
Install tsx as a dev dependency for running TypeScript:
npm install -D 'tsx@^4.7.0' --legacy-peer-depsConfigure the project
Update the scripts section in package.json to add a dev script:
"scripts": {
"dev": "tsx src/index.ts",
"dev:mastra": "mastra dev",
"build": "mastra build",
"start": "mastra start"
},Make sure the project has the following structure:
src/
├── config/
│ └── mcp-server.ts # MCP server configuration
├── mastra/
│ ├── agents/
│ │ └── mcp-agent.ts # Agent with MCP tools
│ ├── workflows/
│ │ └── mcp-workflow.ts # Workflow definition
│ └── index.ts # Mastra instance
└── index.ts # Entry pointThis follows Mastra’s recommended organization: the mastra/ directory contains agents and workflows, the configuration is in config/, and the entry point orchestrates everything.
Adding the MCP server configuration
In src/config/mcp-server.ts, add the following code to configure the connection to your Gram-hosted MCP server:
import { MCPClient } from "@mastra/mcp";
import dotenv from "dotenv";
import { resolve } from "path";
dotenv.config({ path: resolve(process.cwd(), ".env.local") });
export const gramMcpClient = new MCPClient({
servers: {
PushAdvisor: {
url: new URL("https://app.getgram.ai/mcp/your-mcp-server-slug"),
requestInit: {
headers: {
Authorization: `Bearer ${process.env.GRAM_KEY || ""}`,
},
},
},
},
});Replace your-mcp-server-slug with your actual Gram MCP server slug.
The MCPClient class connects to MCP servers and handles protocol negotiation automatically. The configuration loads environment variables first with dotenv.config(), so GRAM_KEY is available, then defines a server named PushAdvisor with its URL and Bearer token authentication. When you call methods like getTools(), the client connects to the server and discovers available tools.
Adding the agent configuration
In src/mastra/agents/mcp-agent.ts, add an agent that can use the MCP server tools. The agent processes questions and decides which tools to call.
import { Agent } from "@mastra/core/agent";
import { openai } from "@ai-sdk/openai";
import { gramMcpClient } from "../../config/mcp-server";
let mcpAgentInstance: Agent | null = null;
export async function getMcpAgent(): Promise<Agent> {
if (!mcpAgentInstance) {
const tools = await gramMcpClient.getTools();
mcpAgentInstance = new Agent({
name: "GramMCPAgent",
instructions:
"You are a helpful assistant that uses the CanIPushToProd MCP server tools to answer questions about pushing to production.",
model: openai("gpt-4o-mini"),
tools,
});
}
return mcpAgentInstance;
}The code uses a singleton pattern to cache the agent instance, avoiding the cost of recreating it on every call. The getMcpAgent() function fetches tools from the MCP client using getTools(), then creates an agent with gpt-4o-mini as the model (which supports the function calling needed for tool usage). The instructions property is the system prompt that guides the agent’s behavior. The agent automatically decides when to call tools based on the user’s question.
Adding the workflow definition
A Mastra workflow defines how an application processes requests. Add the following code in src/mastra/workflows/mcp-workflow.ts:
import { createWorkflow, createStep } from "@mastra/core/workflows";
import { getMcpAgent } from "../agents/mcp-agent";
import { z } from "zod";
import { mastra } from "../index";
const processStep = createStep({
id: "check-push-day",
description:
"Check if it's a good day to push to production using MCP server tools",
inputSchema: z.object({
input: z.string(),
}),
outputSchema: z.object({
output: z.string(),
}),
execute: async ({ inputData }) => {
const agent = await getMcpAgent();
const result = await agent.streamLegacy(
`Is it a good day to push today? Use the PushAdvisor MCP server tools to check if today is a good day to push to production.`,
);
let text = "";
for await (const chunk of result.textStream) {
text += chunk;
}
return { output: text };
},
});
export const mcpWorkflow = createWorkflow({
id: "mcp-workflow",
description: "Workflow that checks if it's a good day to push to production",
inputSchema: z.object({
input: z.string().describe("The input question"),
}),
outputSchema: z.object({
output: z.string(),
}),
mastra,
})
.then(processStep)
.commit();The createStep function defines a workflow step with Zod schemas for input and output validation. The step’s execute function gets the agent and calls streamLegacy() with a prompt instructing the agent to use MCP tools. The code uses streamLegacy() because gpt-4o-mini is an AI SDK v4 model — for v5 models, use generate() instead. The response streams chunk by chunk and is collected into a complete string before returning. The createWorkflow() function defines the workflow with its own schemas, chains the step with .then(), and finalizes with .commit().
Creating the entry point
The entry point is where the application starts. Add the following code in src/index.ts:
import dotenv from "dotenv";
import { resolve } from "path";
import { mcpWorkflow } from "./mastra/workflows/mcp-workflow";
dotenv.config({ path: resolve(process.cwd(), ".env.local") });
async function main() {
const input = process.argv[2] || "Is it a good day to push today?";
console.log("Starting Mastra workflow with Gram MCP server...");
console.log(`Input: ${input}\n`);
const run = await mcpWorkflow.createRunAsync();
const result = await run.start({
inputData: { input },
});
if (result.status === "success") {
console.log("Workflow completed successfully!");
console.log(`Output: ${result.result.output}\n`);
} else {
console.error(
`Workflow failed: ${result.status === "failed" ? result.error : "Unknown error"}\n`,
);
process.exit(1);
}
}
if (import.meta.url === `file://${process.argv[1]}`) {
main().catch(console.error);
}
export { mcpWorkflow };Environment variables load at the top level, so they’re available when other modules import them. The main() function takes input from command-line arguments or uses a default question, creates a workflow run with createRunAsync(), and executes it with run.start(). The result object contains either the output on success or an error on failure. The final if statement ensures that main() only runs when the file is executed directly, not when it’s imported as a module.
Make sure the src/mastra/index.ts file contains the following code:
import { Mastra } from "@mastra/core";
export const mastra = new Mastra();Testing the project
Run the application:
npm run dev "Is it a good day to push today?"This uses tsx to run TypeScript directly without compilation. The question is passed as a command-line argument and becomes the workflow input.
You should see an output like the following:
Starting Mastra workflow with Gram MCP server...
Input: Is it a good day to push today?
Workflow completed successfully!
Output: Yes, today is a good day to push to production! It's Monday, which is considered safe for deployments.The exact output depends on the MCP server’s response and how the agent interprets it.
Here’s what happens when the workflow runs:
- The entry point loads environment variables and creates a workflow run.
- The workflow step gets the agent, which triggers the MCP client to connect to the server and to fetch available tools.
- The agent analyzes the question and calls the appropriate MCP tool (like
can_i_push_to_prod). - The tool runs on the server and returns a result, which the agent uses to generate a natural-language response.
Troubleshooting
Let’s go through some common issues and how to fix them.
Connection errors
If you see connection errors:
- Check that you’ve set the
GRAM_KEYcorrectly in.env.local(check for typos, extra spaces, or missing quotes). - Confirm that the MCP server URL is correct and the server is accessible.
Model compatibility
If you see model compatibility errors:
- Use
streamLegacy()for AI SDK v4 models likegpt-4o-mini. - For AI SDK v5 models, use
generate()instead. - See the Mastra model documentation for compatibility details.
Last updated on