Using Pydantic AI with Gram-hosted MCP servers
Pydantic AI supports MCP servers through the pydantic-ai-mcp-client library. This allows you to give your Pydantic AI agents direct access to your tools and infrastructure by connecting to Gram-hosted MCP servers.
This guide shows you how to connect Pydantic AI to a Gram-hosted MCP server using an example Push Advisor API . You’ll learn how to create an MCP server from an OpenAPI document, set up the connection, configure authentication, and use natural language to query the example API.
Find the full code and OpenAPI document in the Push Advisor API repository .
Prerequisites
You’ll need:
- A Gram account
- An OpenAI API key or Anthropic API key
- A Python environment set up on your machine (using Python 3.9 or a more recent version)
- Basic familiarity with Python and making API requests
Creating a Gram-hosted MCP server
If you already have a Gram-hosted MCP server configured, you can skip to connecting Pydantic AI to your Gram-hosted MCP server.
For this guide, we’ll use the public server URL https://app.getgram.ai/mcp/canipushtoprod.
For authenticated servers, you’ll need an API key. Generate an API key in the Settings tab. For an in-depth guide to how Gram works and to creating a Gram-hosted MCP server, check out our introduction to Gram.
Connecting Pydantic AI to your Gram-hosted MCP server
Pydantic AI supports MCP servers through built-in MCP support using the MCPServerStreamableHTTP class. Here’s how to connect to your Gram-hosted MCP server.
Installation
First, install the required packages:
pip install pydantic-ai python-dotenvEnvironment setup
Set up your environment variables by creating a .env file:
OPENAI_API_KEY=your-openai-api-key-here
ANTHROPIC_API_KEY=your-anthropic-api-key-here # If using Anthropic
GRAM_API_KEY=your-gram-api-key-here # For authenticated serversLoad these in your code:
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()To run the async code given in the sections to follow, you can import asyncio and wrap the code in an async function definition as shown below:
import asyncio
async def main():
# wrap async code
# ................
asyncio.run(main())Basic connection (public server)
Here’s a basic example using a public Gram-hosted MCP server with Streamable HTTP transport:
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from pydantic_ai import Agent
from pydantic_ai.mcp import MCPServerStreamableHTTP
from pydantic_ai.models.openai import OpenAIModel
# Load environment variables
load_dotenv()
# Create an MCP server connection to a public Gram server
mcp_server = MCPServerStreamableHTTP(
url="https://app.getgram.ai/mcp/canipushtoprod"
)
# Create a Pydantic AI agent with MCP server as a toolset
agent = Agent(
model=OpenAIModel("gpt-4o"),
toolsets=[mcp_server] # Pass MCP server via toolsets
)
async with agent: # Open connection to MCP server
# Use the agent
result = await agent.run("What's the vibe today? Use the vibe_check tool.")
print(result.output)Authenticated connection
For private MCP servers, include your Gram API key in the headers:
import os
from pydantic_ai import Agent
from pydantic_ai.mcp import MCPServerStreamableHTTP
from pydantic_ai.models.anthropic import AnthropicModel
GRAM_API_KEY = os.getenv("GRAM_API_KEY")
if not GRAM_API_KEY:
raise ValueError("Missing GRAM_API_KEY environment variable")
# Create an authenticated MCP server connection
mcp_server = MCPServerStreamableHTTP(
url="https://app.getgram.ai/mcp/canipushtoprod",
headers={"Authorization": f"Bearer {GRAM_API_KEY}"}
)
# Create an agent with Claude and MCP server as toolset
agent = Agent(
model=AnthropicModel("claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022"),
toolsets=[mcp_server]
)
async with agent:
# Use the agent
result = await agent.run("Can I push to production today?")
print(result.output)Understanding the configuration
Here’s what each parameter in the MCPServerStreamableHTTP configuration does:
urladds your Gram-hosted MCP server URL.headersadds optional HTTP headers for authentication.
The server uses Streamable HTTP transport, which is compatible with Gram’s HTTP-based MCP servers.
Working with tool responses
Pydantic AI provides detailed information about tool usage in agent responses:
from pydantic_ai import Agent
from pydantic_ai.mcp import MCPServerStreamableHTTP
from pydantic_ai.models.openai import OpenAIModel
# Create MCP server connection
mcp_server = MCPServerStreamableHTTP(
url="https://app.getgram.ai/mcp/canipushtoprod"
)
# Create agent with MCP server as toolset
agent = Agent(
model=OpenAIModel("gpt-4o"),
toolsets=[mcp_server]
)
async with agent:
# Run with detailed response
result = await agent.run("Can I push to production today?")
# Access the response data
print(f"Response: {result.output}")
# Access tool call information
for message in result.all_messages():
if hasattr(message, 'parts'):
for part in message.parts:
if hasattr(part, 'tool_name'):
print(f"Tool called: {part.tool_name}")
if hasattr(part, 'args'):
print(f"Arguments: {part.args}")Streaming responses
Pydantic AI supports streaming responses with MCP tools:
from pydantic_ai import Agent
from pydantic_ai.mcp import MCPServerStreamableHTTP
from pydantic_ai.models.openai import OpenAIModel
# Create MCP server connection
mcp_server = MCPServerStreamableHTTP(
url="https://app.getgram.ai/mcp/canipushtoprod"
)
# Create agent with MCP server as toolset
agent = Agent(
model=OpenAIModel("gpt-4o"),
toolsets=[mcp_server]
)
async with agent:
# Stream the response
async with agent.run_stream("What's the deployment status?") as stream:
async for chunk in stream.stream():
print(chunk, end="", flush=True)Using structured outputs
Pydantic AI excels at structured outputs, which you can combine with MCP tools:
from pydantic import BaseModel
from pydantic_ai import Agent
from pydantic_ai.mcp import MCPServerStreamableHTTP
from pydantic_ai.models.openai import OpenAIModel
class DeploymentDecision(BaseModel):
can_deploy: bool
reason: str
vibe: str
# Create MCP server connection
mcp_server = MCPServerStreamableHTTP(
url="https://app.getgram.ai/mcp/canipushtoprod"
)
# Create agent with structured output
agent = Agent(
OpenAIModel("gpt-4-turbo"),
output_type=DeploymentDecision,
toolsets=[mcp_server]
)
async with agent:
result = await agent.run(
"Check if I can deploy today and what the vibe is"
)
# Access structured data
decision = result.output
print(f"Can deploy: {decision.can_deploy}")
print(f"Reason: {decision.reason}")
print(f"Vibe: {decision.vibe}")Error handling
Pydantic provides an McpError class for handling errors from MCP servers. You can catch this error to handle issues like connection failures or invalid requests:
import os
from pydantic_ai import Agent
from pydantic_ai.mcp import MCPServerStreamableHTTP, McpError
from pydantic_ai.models.openai import OpenAIModel
from pydantic_ai.exceptions import AgentRunError
import httpx
GRAM_API_KEY = os.getenv("GRAM_API_KEY")
def extract_root_cause(exception):
"""Extract the root cause from nested ExceptionGroups"""
if hasattr(exception, 'exceptions') and exception.exceptions:
for sub_exception in exception.exceptions:
root = extract_root_cause(sub_exception)
if root:
return root
else:
return exception
return None
async def create_mcp_agent():
try:
# Create MCP server connection
headers = {"Authorization": f"Bearer {GRAM_API_KEY}"} if GRAM_API_KEY else {}
mcp_server = MCPServerStreamableHTTP(
url="https://app.getgram.ai/mcp/canipushtoprod",
headers=headers
)
# Create agent
agent = Agent(
OpenAIModel("gpt-4o"),
toolsets=[mcp_server]
)
return agent
except Exception as e:
print(f"Failed to create MCP agent: {e}")
return None
async def run_agent_with_error_handling(agent, query):
"""Run agent with comprehensive error handling"""
try:
async with agent:
result = await agent.run(query)
return result.output
except ExceptionGroup as eg:
# Handle nested exception groups from MCP
root_cause = extract_root_cause(eg)
if isinstance(root_cause, httpx.ConnectError):
return "Connection failed: Unable to reach MCP server."
elif isinstance(root_cause, httpx.HTTPStatusError):
if root_cause.response.status_code == 401:
return "Authentication failed: Invalid or missing API key."
elif root_cause.response.status_code == 404:
return "MCP server not found."
elif root_cause.response.status_code >= 500:
return f"Server error: HTTP {root_cause.response.status_code}"
else:
return f"HTTP error: {root_cause.response.status_code}"
elif isinstance(root_cause, McpError):
return f"MCP protocol error: {root_cause}"
elif isinstance(root_cause, TimeoutError):
return "Timeout error: MCP server took too long to respond."
else:
return f"Unexpected error: {type(root_cause).__name__}: {root_cause}"
except AgentRunError as are:
return f"Agent execution error: {are}"
except Exception as e:
return f"Unexpected error: {type(e).__name__}: {e}"
# Usage example
agent = await create_mcp_agent()
if agent:
result = await run_agent_with_error_handling(agent, "What's the vibe?")
print(result)
else:
print("Failed to create agent")Using instructions with MCP tools
Pydantic AI allows you to combine instructions with MCP tools for more controlled behavior:
from pydantic_ai import Agent
from pydantic_ai.mcp import MCPServerStreamableHTTP
from pydantic_ai.models.openai import OpenAIModel
# Create MCP server connection
mcp_server = MCPServerStreamableHTTP(
url="https://app.getgram.ai/mcp/canipushtoprod"
)
agent = Agent(
OpenAIModel("gpt-4-turbo"),
instructions=(
"You are a deployment advisor. Always be cautious and "
"consider the day of the week and current vibe when "
"making deployment recommendations."
),
toolsets=[mcp_server]
)
async with agent:
result = await agent.run("Should we deploy the new feature?")
print(result.output)Using dependencies with MCP tools
Pydantic AI’s dependency injection works with MCP tools:
from dataclasses import dataclass
from pydantic_ai import Agent, RunContext
from pydantic_ai.mcp import MCPServerStreamableHTTP
from pydantic_ai.models.openai import OpenAIModel
@dataclass
class DeploymentContext:
team: str
environment: str
user: str
# Create MCP server connection
mcp_server = MCPServerStreamableHTTP(
url="https://app.getgram.ai/mcp/canipushtoprod"
)
agent = Agent(
OpenAIModel("gpt-4-turbo"),
deps_type=DeploymentContext,
toolsets=[mcp_server]
)
# Use the agent with dependencies
context = DeploymentContext(
team="backend",
environment="production",
user="alice"
)
async with agent:
result = await agent.run(
f"Can {context.user} from {context.team} deploy to {context.environment}?",
deps=context
)
print(result.output)Complete example
Here’s a complete example that demonstrates connecting to a Gram-hosted MCP server and using it with Pydantic AI:
import os
import asyncio
from typing import Optional
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from pydantic import BaseModel
from pydantic_ai import Agent
from pydantic_ai.mcp import MCPServerStreamableHTTP
from pydantic_ai.models.openai import OpenAIModel
# Load environment variables
load_dotenv()
class DeploymentAnalysis(BaseModel):
"""Structured output for deployment analysis"""
can_deploy: bool
risk_level: str # "low", "medium", "high"
reason: str
recommendations: list[str]
async def main():
# Set up environment variables
GRAM_API_KEY = os.getenv("GRAM_API_KEY")
OPENAI_API_KEY = os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")
if not OPENAI_API_KEY:
raise ValueError("Missing OPENAI_API_KEY environment variable")
# Configure MCP server
headers = {"Authorization": f"Bearer {GRAM_API_KEY}"} if GRAM_API_KEY else {}
mcp_server = MCPServerStreamableHTTP(
url="https://app.getgram.ai/mcp/canipushtoprod",
headers=headers
)
try:
# Create an agent with structured output
agent = Agent(
OpenAIModel("gpt-4-turbo"),
output_type=DeploymentAnalysis,
instructions=(
"You are a deployment advisor that provides detailed "
"analysis of deployment readiness."
),
toolsets=[mcp_server]
)
# Test queries
queries = [
"Analyze if we can deploy today",
"What's the risk of deploying on Friday?",
"Check deployment viability for a critical update"
]
async with agent:
print(f"Connected to MCP server")
for query in queries:
print(f"\n📝 Query: {query}")
# Run the agent
result = await agent.run(query)
analysis = result.output
# Print structured results
print(f"💬 Can Deploy: {analysis.can_deploy}")
print(f"⚠️ Risk Level: {analysis.risk_level}")
print(f"📊 Reason: {analysis.reason}")
print(f"💡 Recommendations:")
for rec in analysis.recommendations:
print(f" - {rec}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error: {e}")
# Run the example
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())Differences from other MCP integrations
Pydantic AI’s approach to MCP differs from other frameworks:
Connection method
- Pydantic AI uses
MCPServerStreamableHTTPastoolsets. - LangChain uses
MultiServerMCPClientwith multiple servers. - OpenAI uses a
toolsarray withtype: "mcp"in the Responses API. - Anthropic uses
mcp_serversparameter in the Messages API. - The Vercel AI SDK uses
experimental_createMCPClient.
Type safety
- Pydantic AI offers strong type safety with Pydantic models for structured outputs.
- LangChain offers dynamic typing with tool discovery.
- Others offer basic type support without structured output capabilities.
Framework features
- Pydantic AI includes dependency injection, structured outputs, and type validation.
- LangChain includes workflow abstractions, chains, and multi-server support.
- Others are limited to direct API usage without additional abstractions.
Transport support
- Pydantic AI supports Streamable HTTP transport for remote servers.
- LangChain supports both
streamable_httpandstdiotransports. - The Vercel AI SDK supports SSE, stdio, and custom transports.
- Others use direct HTTP connections.
Testing your integration
If you encounter issues during integration, follow these steps to troubleshoot:
Validate MCP server connectivity
Before integrating into your application, test your Gram-hosted MCP server in the Gram Playground to ensure the tools work correctly.
Use the MCP Inspector
Anthropic provides an MCP Inspector command line tool that helps you test and debug MCP servers before integrating them with Pydantic AI. You can use it to validate your Gram-hosted MCP server’s connectivity and functionality.
Run the following command to test your Gram-hosted MCP server with the Inspector:
# Install and run the MCP Inspector
npx -y @modelcontextprotocol/inspectorIn the Transport Type field, select Streamable HTTP.
Enter your server URL in the URL field, for example:
https://app.getgram.ai/mcp/canipushtoprodClick Connect to establish a connection to your MCP server.
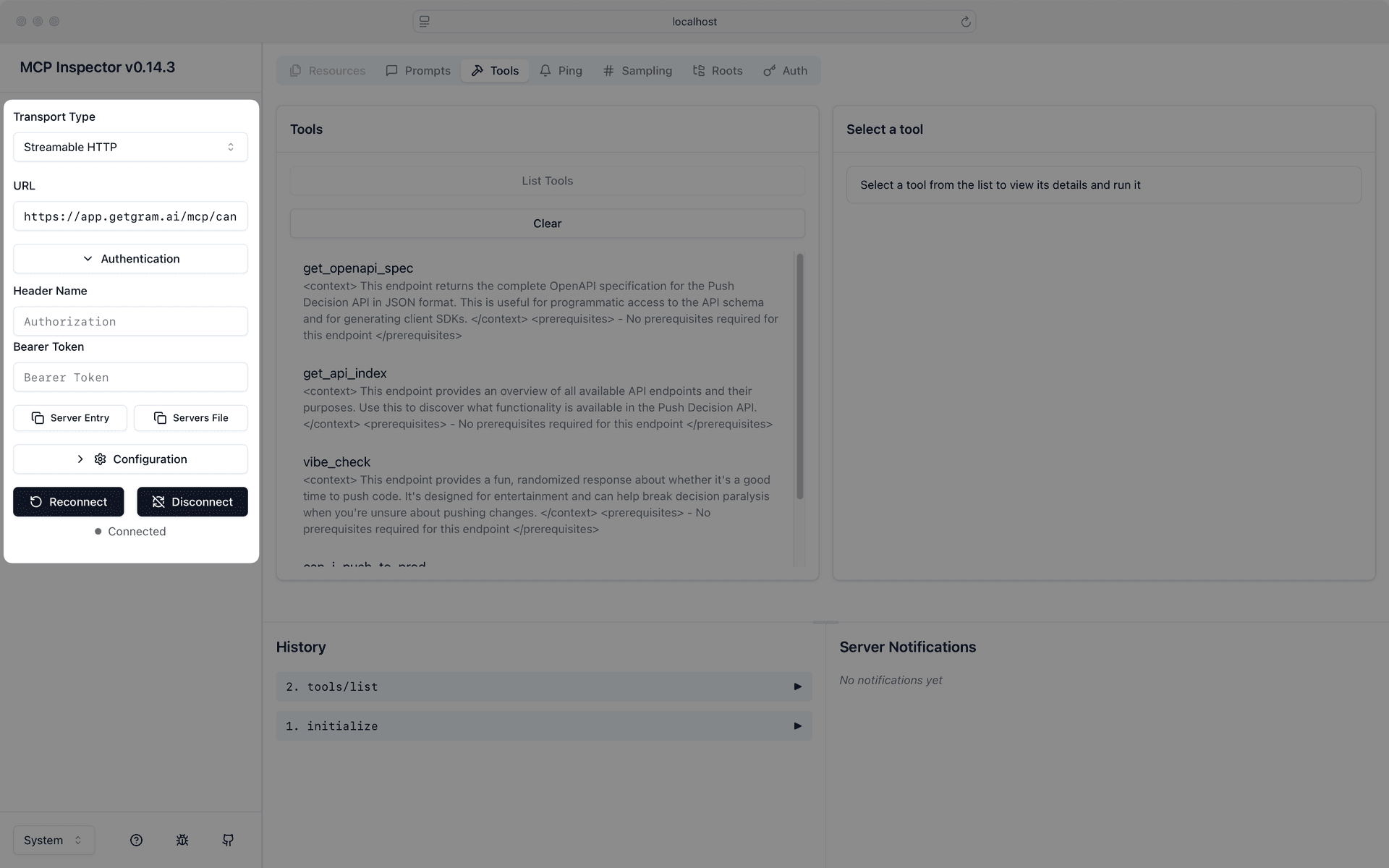
Use the Inspector to verify that your MCP server responds correctly before integrating it with your Pydantic AI application.
Debug tool discovery
You can debug which tools are available from your MCP server by inspecting the agent after creation:
import asyncio
from pydantic_ai import Agent
from pydantic_ai.mcp import MCPServerStreamableHTTP
from pydantic_ai.models.openai import OpenAIModel
async def list_tools():
# Create MCP server connection
mcp_server = MCPServerStreamableHTTP(
url="https://app.getgram.ai/mcp/canipushtoprod"
)
# Create agent
agent = Agent(
OpenAIModel("gpt-4o"),
toolsets=[mcp_server]
)
async with agent:
# Agent is now connected and tools are available
print("MCP server connected successfully")
print("You can now run queries that will use the available tools")
asyncio.run(list_tools())Environment setup
Ensure your environment variables are properly configured:
# .env file
OPENAI_API_KEY=your-openai-api-key-here
ANTHROPIC_API_KEY=your-anthropic-api-key-here # If using Anthropic
GRAM_API_KEY=your-gram-api-key-here # For authenticated serversThen load them in your application:
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()What’s next
You now have Pydantic AI connected to your Gram-hosted MCP server, giving your agents access to your custom APIs and tools with the power of type-safe, structured outputs.
Pydantic AI’s focus on type safety, structured outputs, and dependency injection makes it ideal for building robust, production-ready AI applications that can reliably interact with your infrastructure.
Ready to build your own MCP server? Try Gram today and see how easy it is to turn any API into agent-ready tools that work with Pydantic AI and all major AI frameworks.
Last updated on